Carbohydrates
are a group of substances that are important in many biological processes. they provide energy-rich nutrients to organisms and are used to build their body structure.
Monosacharides are simple sugars, and they have the common formula (CH2O)n Where letter can be any number from 3 to 7. Glucose is a simple sugar where n is 6 so the formula is C6H12O6.Plants produce glucose with photosynthesis.
.jpg)
Glucose has different issomers, they are alpha glucose and beta glucose. The figure in the left shows the difference in the structures. Beta Glucose can be digested by herbivores because they produce cellulase,so carnivores can not digest beta glucose.
Disacharides are the combination of two monosacharides, they are produced by a condensation reaction . The bond formed is called glycosidic bond.
- Maltose: (malt sugar) is a disacharide made up of two glucose molecules
- Sucrose: (table sugar) is made up of a glucose and fructose.
- Lactose: (milk sugar) is made up of a glucose and a galactose.
Disacharides can be broken down to the constituent monosacharide by hydrolisis.
A reducing sugar is any sugar that, in basic solution, forms some aldehyde or ketone. This allows the sugar to act as a reducing agent, for example in the Maillard reaction and Benedict's reaction.
Here are some of them: Glucose, fructose, glyceraldehyde, lactose, arabinose and maltose
The non reducing sugars are: sucrose and trehalose
Functions of simple sugars in living organisms
Lactose is the main sugar of the milk
- maltose it is produced by the breakdown of amylose in many germinating seeds.
- sucrose is the form in which carbohydrates are transported in plants.
- glucose is the main source of energy for most animals (19kj of energy), and it is also the main form in which carbohydrates are transported in animals
Reducing sugars:


(alpha & beta)





Polysacharides A molecule with between 3 and 10 monosacharides units is called an oligosacharides. If more and more units are added, it is called a polysacharides, this happens by a process called polymerisation. A polymer is a large molecule of repeating units that are called monomers. Conjugated molecules are molecules formed by monosacharides monomers with other type of molecules. They have the general formula of (C6H10O5)n
There are two differents glycosidic bonds: the 1-4 glycosidic bond is the condensation reaction between the hydroxl groups at carbon 1 of one monosacharide and carbon 4 of an other. The 1-6 glycosidic bond is formed y the condensation reaction of teh hydroxyl group atcarbon 1 and at 6 of the other.
- Straight chains are formed by monomers linked by 1-4 glycosidic bonds
- Branched chains are formed by monomers linked by 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Starch: is the way in which energy is storage in plants. It is a polysacharide formed by alpha glucose units. Starch consist in two components, amylose and amylopectin. In amylose, the units are linked by 1-4 glycosedic bonds forming a straight chain. In amylopectin, the units are linked by 1-6 glycosidic bonds forming a branched chain. Because of the compact structure, starch is ideal for storage. It is a helical molecule with the hydroxil groups pointing inwards.
Glycogen is the way in which energy is storage in animals. It is abundant in liver and muscle cells. It is very similar to starch but it is much more branchd because it has more 1-6 glycosidic bonds.
Cellulose is the the main components of the cell walls. It carries a structural functions in plants. Cellulose is completely permeable. In comparison with starch and glycogen, cellulose isn't easy to hydrolysed so herbivores are the only animals that can digest it because it have microorganisms that produce an enzime called cellulase.
Lignin is what makes cellulose further strengthened in wood. It is a highly complex non carbohydrate polymer. It impregnates in th cell walls of the xylem vessels in a process called lignification, when the cell wall is completely lignificated, it dies. Also this prevent decay and rot infections.




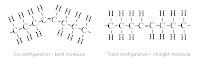
.jpg)






