Compounds wich are insoluble in water but dissolve readily in other lipids or organic solvents (ethanol,chloromethanol). All lipids contain carbon,hydrogen and oxygen wich is lower than in carbohydrates.

Triglycerides, are also known as true fats, are lipids made from a molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acids. They are formed by a condensation reaction, water is removed forming a bond called "ester bond".
Fatty acids may be saturated or unsaturated. The saturated fatty acids are the ones that have no any free electrons to form any new bond, they have only single bonds. The unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds of carbo that could break for creating new bonds, they are qualified into monounsaturated fatty acids that have only one double bond, and the polyunsaturated fatty acids that have two or more doble bonds.
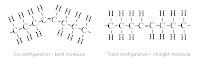
In the unsatureted fatty acids there are the cis-fatty acids that is liquid because the hidrocarbon chain is not totally straight so the atracctions between the molecules is very weak. And there are also the trans-fatty acids which are much more solid because hidrocarbon chains are satright so it leads to the properties of saturated fatty acids.
Functions of Fats and Oils in living organisms
Tryglicerols, for example, they have the higher proportion of hidrogen either carbohydrates or proteins, so they are the a more concentrated source of energy. Under the skin is the adipose tissue which is a special connective tissue for the storage of fats.
- heat insulation, it manteins the heat and prevent it to go out, in winter the adipose tissue increase
- shock absorption, some organs that are delicate have a thick layer of fats for protection
- buoyancy, oil produced for single-celled aquatic organisms to aid buoyancy
Phospholipids
They form a major part of cell membranesincluding myelin which allows a fast conduction of nerve impulses. Phospholipids consist of a glycerol and two fatty acids chains. The third hydroxyl group combines with phosphoric acid to form a polar phophste group. The polar group is hydrophilic, and the non-polar tail is hydrophobic, that's why it is called amphipathic.
In water they join together forming a layer, in the cells mostly all is water so they form a double layer , with the hydrophobic tails inwards.
.jpg)






